When it comes to joining fiber optic cables, choosing between fusion and mechanical splicing depends on your specific needs. Fusion splicing offers a permanent, low-loss connection ideal for high-performance networks, while mechanical splicing provides a quicker, temporary fix suitable for field repairs. Understanding the differences can help you make the right decision for your application. But which method truly offers the best balance of reliability and convenience?
Key Takeaways
- Fusion splicing permanently joins fibers by melting and fusing cores, offering low loss and high strength.
- Mechanical splicing aligns fibers using a physical connector, allowing for easier, quick, and often temporary connections.
- Fusion splicing requires specialized equipment and precision but provides superior durability and minimal signal loss.
- Mechanical splicing is suitable for temporary or field repairs, with simpler setup but generally higher insertion loss.
- The choice depends on project needs, with fusion favored for long-term, high-performance links, and mechanical for flexibility and speed.
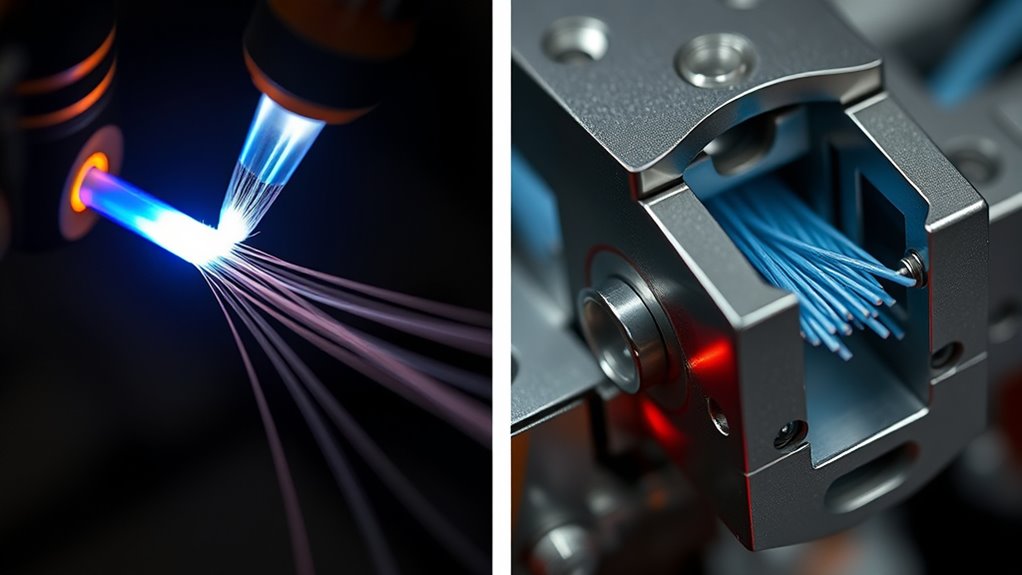
Splicing techniques are essential methods used to join two or more pieces of material seamlessly, guaranteeing strength and durability. Whether you’re working with fibers, cables, or textiles, the way you connect these materials impacts the overall performance and longevity of your project. When considering splicing, one of the most critical factors is fiber alignment. Proper fiber alignment guarantees that the fibers are positioned precisely to maximize strength and minimize weaknesses at the joint. Misaligned fibers can cause stress concentrations, leading to potential failures over time. As you prepare to splice, take your time to guarantee that the fibers are perfectly aligned, matching their cores and maintaining consistent tension throughout the process. This step is crucial in both fusion and mechanical splicing, as it directly influences the quality of the connection. Additionally, understanding the properties of different battery technologies can help in selecting the most suitable splicing method for energy storage applications.
Adhesive selection also plays a vital role in the splicing process, especially when dealing with fiber optics or textiles. The adhesive you choose must be compatible with the materials you’re working with, providing a strong bond without degrading the fibers or compromising flexibility. For fiber optic splicing, adhesives like UV-curable or epoxy resins are commonly preferred because they offer transparency, minimal shrinkage, and high strength. When selecting an adhesive, consider factors like temperature resistance, curing time, and environmental exposure. The right adhesive not only bonds the fibers securely but also protects them from external factors that could cause deterioration. In mechanical splicing, adhesives are often used in conjunction with mechanical fixtures to reinforce the joint and guarantee it withstands mechanical stresses. This careful selection ensures the longevity of your spliced components, especially in outdoor or high-stress environments. Both techniques require careful attention to fiber alignment and adhesive selection, but each offers distinct advantages depending on your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Splicing Method Is More Durable in Outdoor Conditions?
Fusion splicing is more durable outdoors because it offers better weather resistance and UV stability. You’ll find that fusion joints are less prone to environmental damage, making them ideal for outdoor conditions. Mechanical splicing, while easier to install, may degrade faster with exposure to moisture, sunlight, and temperature changes. For long-term outdoor durability, fusion splicing provides a stronger, more resilient connection that withstands harsh weather better.
How Do Splicing Techniques Vary for Different Cable Types?
You’ll find that splicing techniques vary for different cable types, especially with fiber optics and cable insulation. For fiber optics, fusion splicing is common because it creates a seamless, low-loss connection ideal for high-performance needs. Mechanical splicing, on the other hand, suits cables with thicker insulation or where quick repairs are needed. Always consider the cable’s insulation material and performance requirements when choosing your splicing method.
What Safety Precautions Are Essential During Splicing?
You should always wear protective gear, including gloves and safety glasses, to prevent injuries during splicing. Make certain your workspace is well-ventilated to avoid inhaling harmful fumes. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and be mindful of fire safety, especially when working with heat or soldering equipment. Follow proper procedures, avoid distractions, and double-check connections to prevent accidents. Staying vigilant helps keep you safe while ensuring quality splicing.
Can Splicing Methods Be Automated for Large-Scale Projects?
Yes, you can automate splicing methods for large-scale projects, but the automation potential isn’t without hurdles. As you scale up, you’ll encounter significant scalability challenges, like maintaining precision and quality control. Advanced machinery and robotics are increasingly capable of handling fusion or mechanical splicing, yet ensuring consistent results requires careful planning. Stay alert—leveraging automation could revolutionize your workflow, but it demands meticulous integration and oversight to succeed.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Each Splicing Technique?
You should consider that fusion splicing has lower recyclability concerns because it creates a seamless joint, reducing waste. However, it involves chemicals and heat, raising chemical waste management issues. Mechanical splicing is easier to disassemble, making recycling simpler, but it may generate more plastic and material waste during installation. Both techniques impact the environment differently, so weighing recyclability and waste management practices is essential for sustainable choices.
Conclusion
So, whether you’re aiming for perfection with fusion splicing or just need a quick fix with mechanical splicing, remember—one’s a marathon runner, the other’s a sprint. Fusion offers a lasting, high-performance connection, while mechanical’s perfect for when you’re in a hurry or playing field repair. Choose wisely, because in the world of fiber optics, a good splice can either make or break your network—literally. Happy splicing!