When designing a network, choosing the right topology can considerably impact performance, security, and scalability. Each option—star, bus, ring, or mesh—offers distinct advantages and drawbacks that influence how devices connect and communicate. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions for your specific needs. But which topology best balances your priorities? Exploring these options reveals the factors that can shape a network’s effectiveness and resilience.
Key Takeaways
- Star topology connects devices to a central hub, simplifying management and troubleshooting.
- Bus topology links all devices along a single shared medium, offering low setup costs but potential congestion.
- Ring topology forms a circular data path, reducing collisions and improving security through orderly data flow.
- Mesh topology features multiple direct links between devices, providing high reliability and enhanced security.
- Topologies influence network performance, security, scalability, and cost, with centralized designs offering better control.
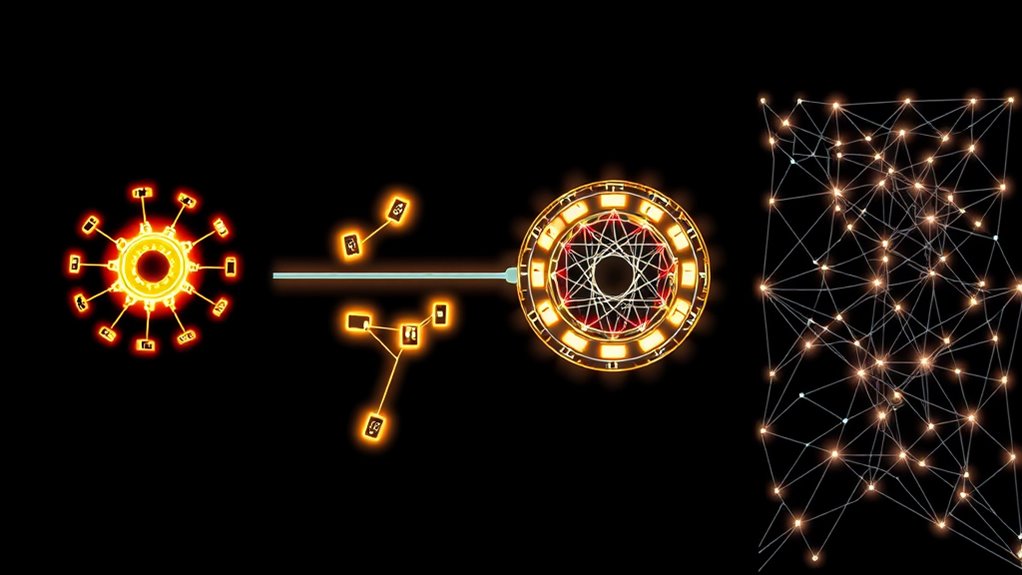
Have you ever wondered how devices in a network connect and communicate efficiently? Understanding network topologies is key to grasping how data flows and how different setups impact performance. One popular topology is the star, where every device connects directly to a central hub or switch. This design makes managing wireless connectivity straightforward because the hub acts as a control point, simplifying troubleshooting and expanding the network. Plus, it enhances network security since traffic passes through the central device, allowing you to monitor and control data more effectively. If a device experiences issues or gets compromised, it doesn’t affect the entire network, making it a resilient choice for maintaining security.
In contrast, the bus topology connects all devices along a single communication line, often called a backbone. While this setup is simple and cost-effective, it can introduce challenges for wireless connectivity, especially as more devices join the network. The shared medium means that data transmission can become congested, leading to slower speeds and potential security vulnerabilities because signals can be intercepted or disrupted more easily. For small networks, the bus topology might suffice, but as your needs grow, it may become less reliable and harder to guarantee against malicious attacks or unauthorized access. Additionally, variety of materials used in network cables can influence performance and security.
The ring topology forms a circle where each device connects to two neighbors, passing data around the ring. This arrangement ensures orderly communication, reducing data collisions, which benefits both wired and wireless connections. Because data flows in one direction or both directions, it’s easier to implement security measures like encryption and access controls, protecting data as it travels around the ring. However, if one connection fails, it can disrupt the entire network unless you incorporate features like dual rings or redundancy. For wireless connectivity, maintaining a stable ring can be challenging but offers good control over data flow, making it easier to detect and prevent security breaches.
Finally, the mesh topology provides multiple paths between devices, creating a highly reliable and secure network. Every device connects directly to several others, ensuring that if one link drops, data can reroute through alternative paths. This setup is ideal for wireless networks where consistent connectivity and high security are priorities. Mesh networks are inherently resilient, making them suitable for environments where network security is critical, such as corporate settings or public Wi-Fi hotspots. The increased complexity and cost may be drawbacks, but the advantages in reliability and security often outweigh these concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Topology Offers the Best Scalability for Large Networks?
You’ll find that a mesh topology offers the best scalability for large network design because it easily accommodates growth. Its scalability comparison shows it handles more devices with minimal performance issues since each device connects directly to others. Although it’s more complex to set up and maintain, mesh networks excel in large environments, ensuring reliable communication and flexibility as your network expands.
How Does Topology Impact Network Security Measures?
Think of your network as a fortress, where topology shapes its defenses. Your choice impacts security vulnerabilities and resilience; for example, a star topology centralizes control, making it easier to monitor but vulnerable if the hub fails. Mesh offers high resilience, reducing vulnerabilities but increasing complexity. Your topology determines how effectively you can implement security measures and respond to threats, shaping your network’s overall strength.
What Are the Cost Differences Among Various Topologies?
You’ll find that hardware costs vary considerably among topologies. Star networks generally cost more initially because they require a central hub and more cabling, but they’re easier to implement and troubleshoot. Bus topologies are cheaper upfront, needing less hardware, but can become complex as the network grows. Ring and mesh topologies tend to have higher implementation complexity and costs due to additional cabling and hardware, especially in large setups.
Can Hybrid Topologies Combine Advantages of Multiple Types?
Yes, hybrid topologies combine the advantages of multiple types through hybrid integration, offering topology flexibility. You can tailor the network to meet specific needs, such as combining star and bus topologies to improve reliability and cost-effectiveness. This approach allows you to optimize performance, scalability, and fault tolerance, making your network more adaptable and resilient to changing requirements or growth.
How Do Topologies Affect Network Troubleshooting and Maintenance?
You find that topology impacts troubleshooting and maintenance considerably. For example, in a star setup, fault isolation is easier, as a single device or connection failure doesn’t affect the whole network, reducing maintenance complexity. Conversely, in a bus or ring topology, identifying faults can be more challenging, potentially increasing troubleshooting time. Choosing the right topology helps streamline maintenance and minimize network downtime.
Conclusion
As you explore network topologies, you’ll find that each one offers unique advantages—like the star’s simplicity, the bus’s cost-effectiveness, the ring’s efficiency, or the mesh’s reliability. Coincidentally, your choice often depends on what you need most: security, speed, or scalability. Sometimes, the best network isn’t about picking one over the others but understanding how these different setups can work together to create a seamless, efficient system tailored just for you.









