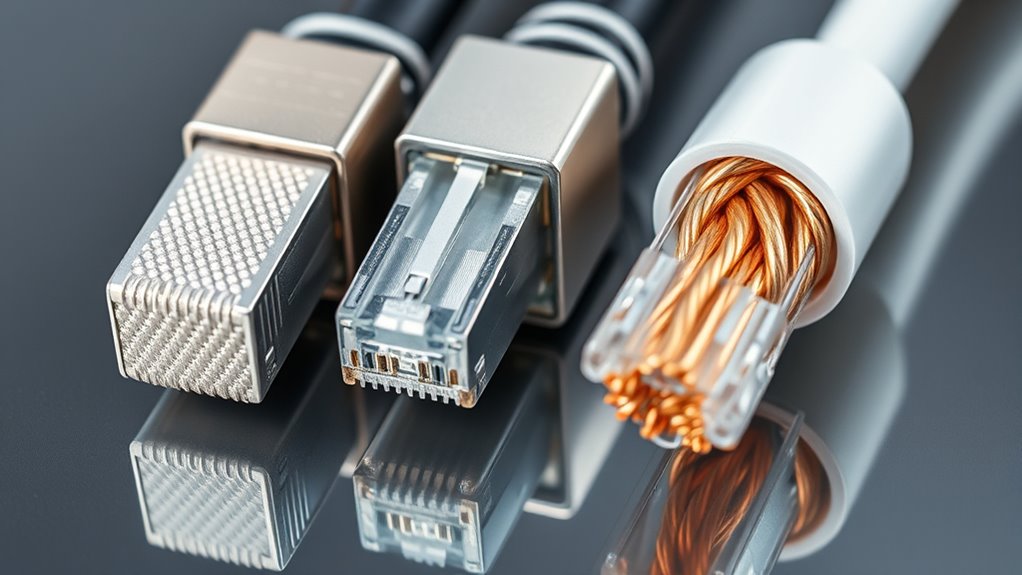
When selecting network cabling, understanding the differences between UTP, FTP, and STP can critically impact your setup’s performance. Each type offers varying levels of protection against electromagnetic interference, which is essential in noisy environments. Without knowing the specifics of your installation space, choosing the right shielding could mean the difference between reliable connectivity and persistent issues. Curious about which option best suits your needs?
Key Takeaways
- UTP has no additional shielding, relying on twisted pairs for noise rejection, suitable for low-interference environments.
- FTP features a foil shield around twisted pairs, offering improved noise immunity over UTP.
- STP combines foil or braid shields around each pair and an overall shield for enhanced protection in high-interference settings.
- Shielding materials like foil provide high-frequency noise protection, while braid shields excel at lower frequencies.
- Proper grounding of shielded cables maximizes noise rejection and prevents interference issues.
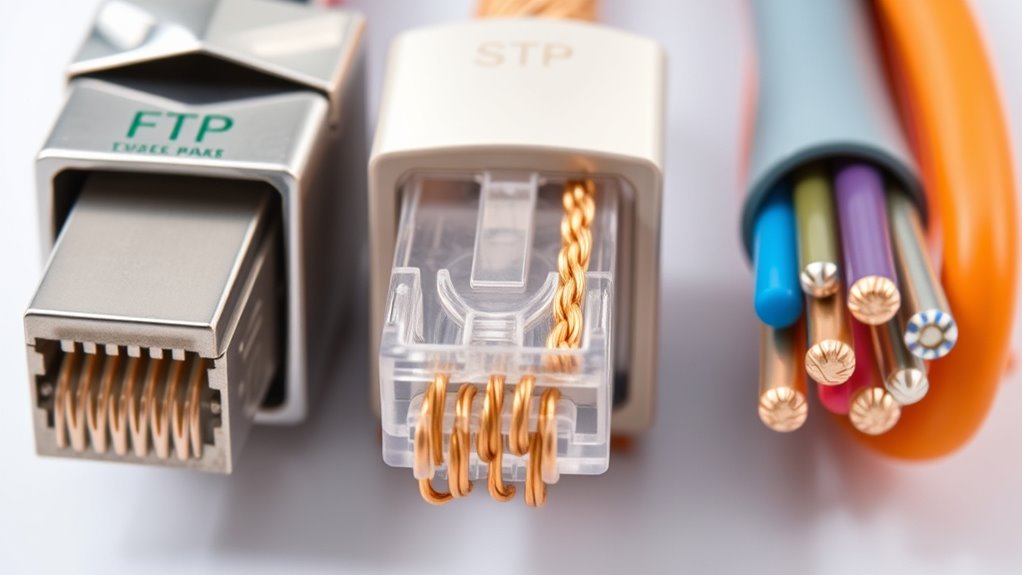
Cable shielding plays a essential role in protecting signals from external interference and preventing signal leakage. When choosing between different shielding types like FTP, STP, and UTP, understanding how grounding techniques and shielding material comparison impact performance is fundamental. Grounding techniques are indispensable because they help dissipate unwanted noise and static that can distort signals. For example, properly grounding a shield can markedly reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). If grounding isn’t handled correctly, even the best shielding material won’t perform at its best, leaving your network vulnerable to interference and data errors.
Shielding material comparison reveals notable differences among FTP, STP, and UTP cables. UTP, or unshielded twisted pair, lacks any additional shielding and relies solely on twisted pairs for noise rejection. While UTP is cost-effective and easy to install, it offers limited protection against external interference, making it less suitable in environments with high EMI. On the other hand, FTP, or foil twisted pair, adds an overall foil shield around the twisted pairs, providing a barrier against external signals. This foil shield, often connected to grounding points, enhances noise immunity, especially in environments with moderate interference. STP, or shielded twisted pair, takes shielding further by wrapping each twisted pair with foil or braid shields and adding an overall shield. This layered approach offers superior protection against EMI and RFI, making STP ideal for industrial or high-interference settings.
When considering shielding material comparison, it’s also important to evaluate the type of shield used. Foil shields are thin and flexible, providing excellent coverage against high-frequency noise but less durability. Braid shields are more durable and offer better coverage against lower-frequency interference but can be less flexible. Combining both in STP cables offers a balanced solution for robust noise rejection. Proper grounding techniques are crucial here; connecting shields to ground at one or both ends ensures that unwanted interference is safely diverted away from your signals. Failing to ground shields correctly can lead to ground loops, which might actually introduce interference rather than prevent it. Additionally, understanding the importance of connection to ground and its role in enhancing shielding effectiveness is vital for optimal performance.

Cable Matters [UL Listed 10Gbps in-Wall (CM) Rated 23AWG Bare Copper Shielded Cat 6A Cable – 1000ft, Solid, S/STP, S/FTP Shielded Cat6a Bulk Ethernet Cable, Cat6a Ethernet Cord, Blue
Shielded Cat6a Bulk Ethernet Cable: CM-rated solid shielded Cat 6A Shielded/Foil Twisted Pair (S/FTP) bulk cable is engineered…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Shielding Types Affect Cable Installation Costs?
Shielding types substantially impact your cable installation costs by influencing the cost comparison and installation complexity. FTP and STP cables, with their additional shielding, tend to be more expensive and harder to install due to their rigidity and extra handling requirements. UTP cables are cheaper and easier to work with, making them ideal for simple setups. Consider your environment and budget to choose the right shielding type, balancing cost and installation effort.
Are There Environmental Factors Influencing Shielding Effectiveness?
Environmental factors like moisture, temperature, and electromagnetic interference can influence shielding effectiveness. You should consider grounding requirements to prevent signal noise, as improper grounding reduces shield performance. Additionally, select shielding materials with high durability to withstand harsh conditions, ensuring long-term protection. By addressing these factors, you improve cable reliability and maintain signal integrity despite challenging environmental conditions.
Can Shielding Types Impact Network Speed and Bandwidth?
Yes, shielding types can impact your network speed and bandwidth by affecting signal integrity and data security. Proper shielding reduces electromagnetic interference, allowing your data to transmit more efficiently without errors. This means faster speeds and more reliable connections. If shielding isn’t adequate, you might experience slower performance or potential security risks. Choosing the right shielding type guarantees your network maintains ideal speed, bandwidth, and protection against external interference.
Which Shielding Type Is Best for Outdoor Applications?
For outdoor applications, STP shielding is your best choice because it offers better material durability and protection against interference and environmental factors. While it may require more installation effort due to its complex setup, it guarantees long-term performance and reliability. UTP is less suitable outdoors because it lacks shielding, making it vulnerable to damage and interference. Choose STP for a balance of durability and effective shielding in outdoor environments.
How Do Shielding Types Influence Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Protection?
Think of shielding types as your cable’s immune system against EMI. For example, STP with proper grounding acts like a shielded helmet, blocking interference effectively. UTP, lacking shielding, is more vulnerable unless grounded well. Shielding influences EMI protection by reducing noise, but you also need durable materials for outdoor use and correct grounding to guarantee maximum effectiveness, especially against strong interference sources.

Jadaol Cat 6 Ethernet Cable 100ft, 10Gbps Support Cat8 Cat7 Network, Flat RJ45 LAN Patch Cable, High-Speed Wired Internet Cable for Router, Modem, Switch, Gaming Consoles, PC, Streaming Devices, White
Cat 6 performance at a Cat5e price but with higher bandwidth. Bundled with the 35 cable clipes,no need…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Conclusion
Now that you understand the differences between UTP, FTP, and STP, you might wonder which shield best suits your environment. Will you choose the cost-effective UTP and risk interference, or opt for the more protective FTP and STP to ensure crystal-clear signals? The choice isn’t just about cost—it’s about safeguarding your data from unseen electromagnetic threats. The decision you make could determine whether your network stays seamless or succumbs to interference when you least expect it.

NavePoint Cat6 (CCA), 1000ft, Blue, Solid Bulk Ethernet Cable, 550MHz, 23AWG 4 Pair, Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
HIGH PERFORMANCE CAT6 ETHERNET CABLE: Designed for home or office networks, supporting 10/100/1000 Mbps speeds. This Cat6 cable,…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.

UGREEN Cat 8 Ethernet Cable 6FT, High Speed Braided 40Gbps 2000Mhz Network Cord Cat8 RJ45 Shielded Indoor Heavy Duty LAN Cables Compatible for Gaming PC PS5 Xbox Modem Router 6FT
40 Gbps 2000 Mhz High Speed: The Cat 8 Ethernet cable support max.40 Gbps data transfer and 2000…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.